天际线问题
问题描述
| Category | Difficulty | Likes | Dislikes |
|---|---|---|---|
| algorithms | Hard (39.25%) | 93 | - |
Tags
divide-and-conquer | heap | binary-indexed-tree | segment-tree | line-sweep
Companies
facebook | google | microsoft | twitter | yelp
城市的 天际线 是从远处观看该城市中所有建筑物形成的轮廓的外部轮廓。给你所有建筑物的位置和高度,请返回 *由这些建筑物形成的**天际线** 。
每个建筑物的几何信息由数组 buildings 表示,其中三元组 buildings[i] = [lefti, righti, heighti] 表示:
left<sub>i</sub>是第i座建筑物左边缘的x坐标。right<sub>i</sub>是第i座建筑物右边缘的x坐标。height<sub>i</sub>是第i座建筑物的高度。
你可以假设所有的建筑都是完美的长方形,在高度为 0 的绝对平坦的表面上。
天际线 应该表示为由 “关键点” 组成的列表,格式 [[x<sub>1</sub>,y<sub>1</sub>],[x<sub>2</sub>,y<sub>2</sub>],...] ,并按 **x 坐标 **进行 排序 。 关键点是水平线段的左端点 。列表中最后一个点是最右侧建筑物的终点,y 坐标始终为 0 ,仅用于标记天际线的终点。此外,任何两个相邻建筑物之间的地面都应被视为天际线轮廓的一部分。
注意: 输出天际线中不得有连续的相同高度的水平线。例如 [...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...] 是不正确的答案;三条高度为 5 的线应该在最终输出中合并为一个:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
示例 1:
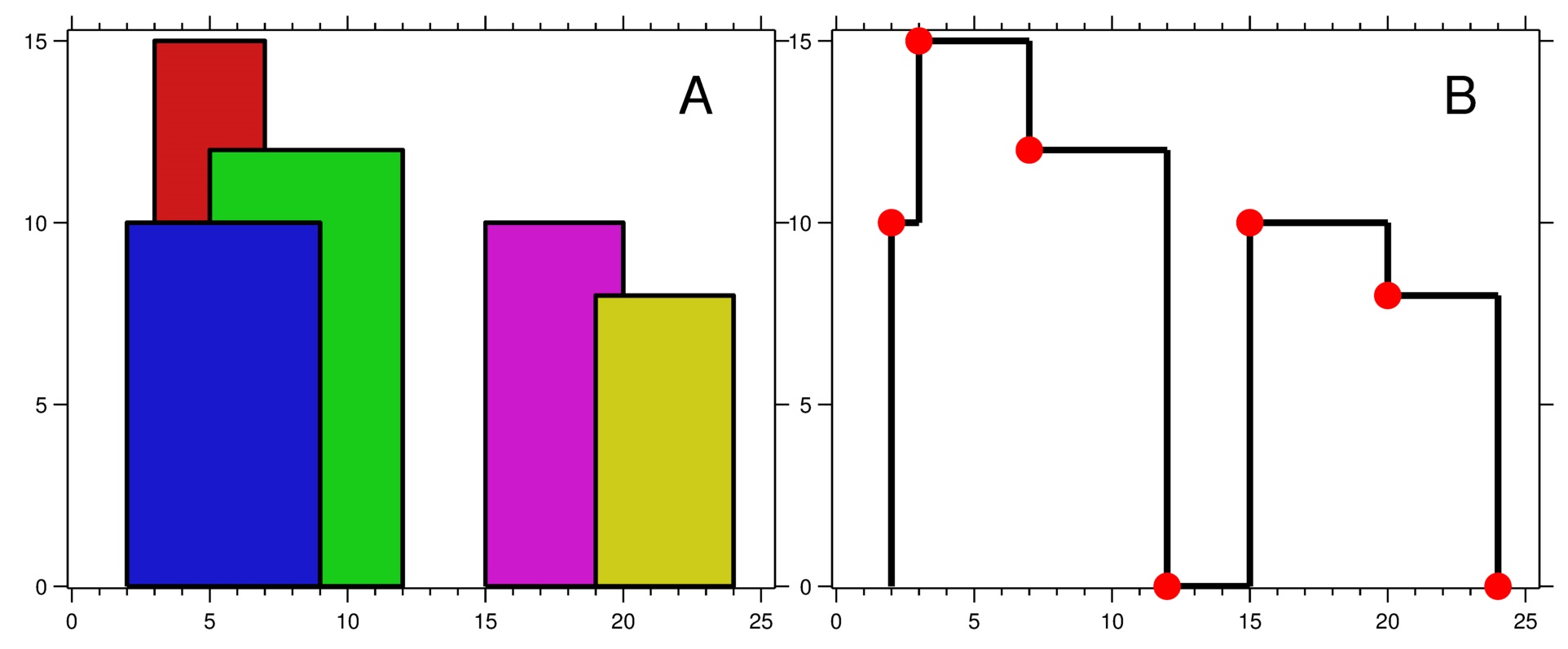
| |
示例 2:
| |
提示:
1 <= buildings.length <= 10<sup>4</sup>0 <= left<sub>i</sub> < right<sub>i</sub> <= 2<sup>31</sup> - 11 <= height<sub>i</sub> <= 2<sup>31</sup> - 1buildings按left<sub>i</sub>非递减排序
说明:
- 任何输入列表中的建筑物数量保证在
[0, 10000]范围内。 - 输入列表已经按左
x坐标Li进行升序排列。 - 输出列表必须按 x 位排序。
- 输出天际线中不得有连续的相同高度的水平线。例如
[...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...]是不正确的答案;三条高度为 5 的线应该在最终输出中合并为一个:[...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
解法
分治+归并
| |
扫描线法
使用扫描线,从左至右扫过。
如果遇到左端点,将高度入优先队列,如果遇到右端点,则将高度从优先队列中删除。
使用 last 变量记录上一个转折点。
可以参考下面的图,扫描线下方的方格就是堆。
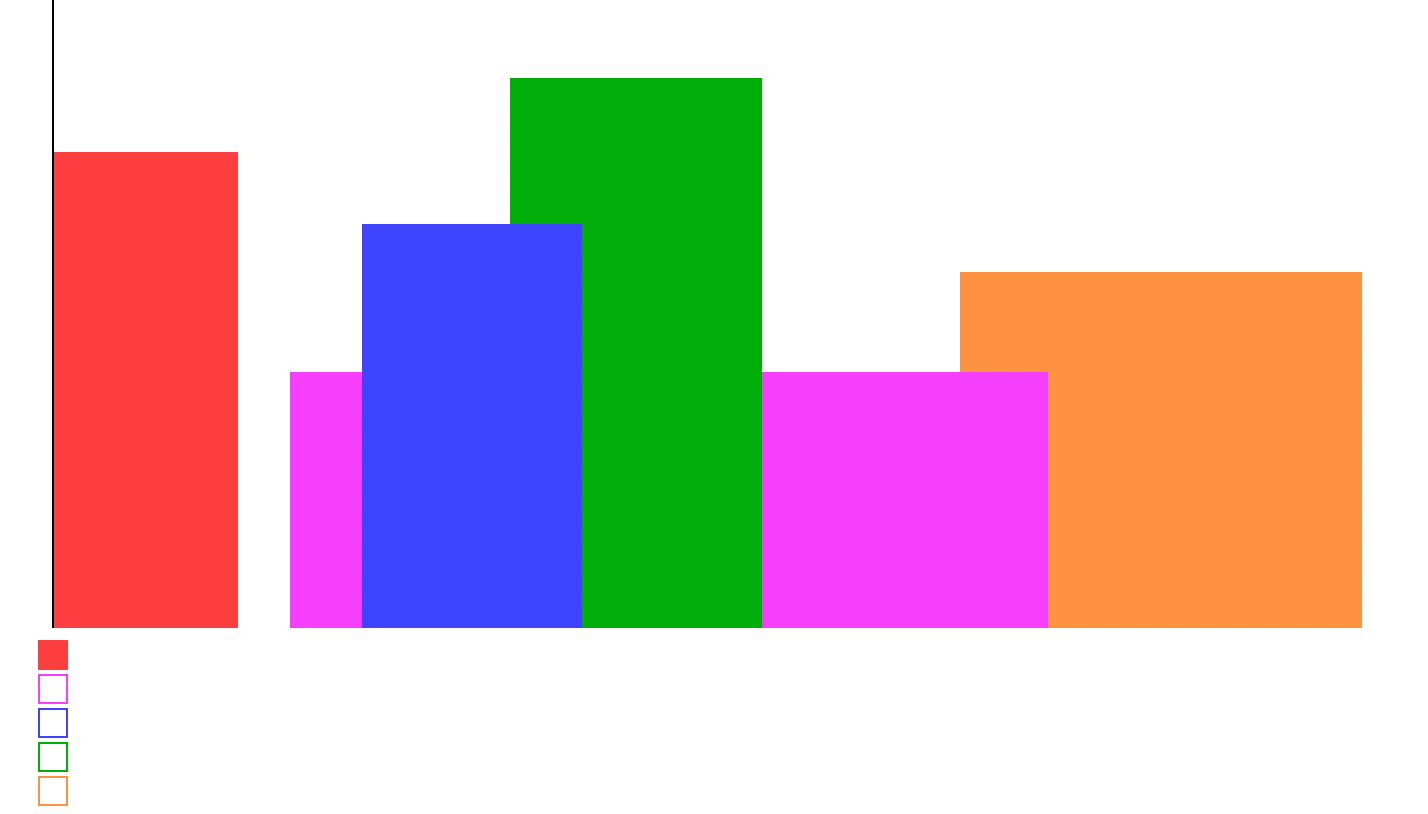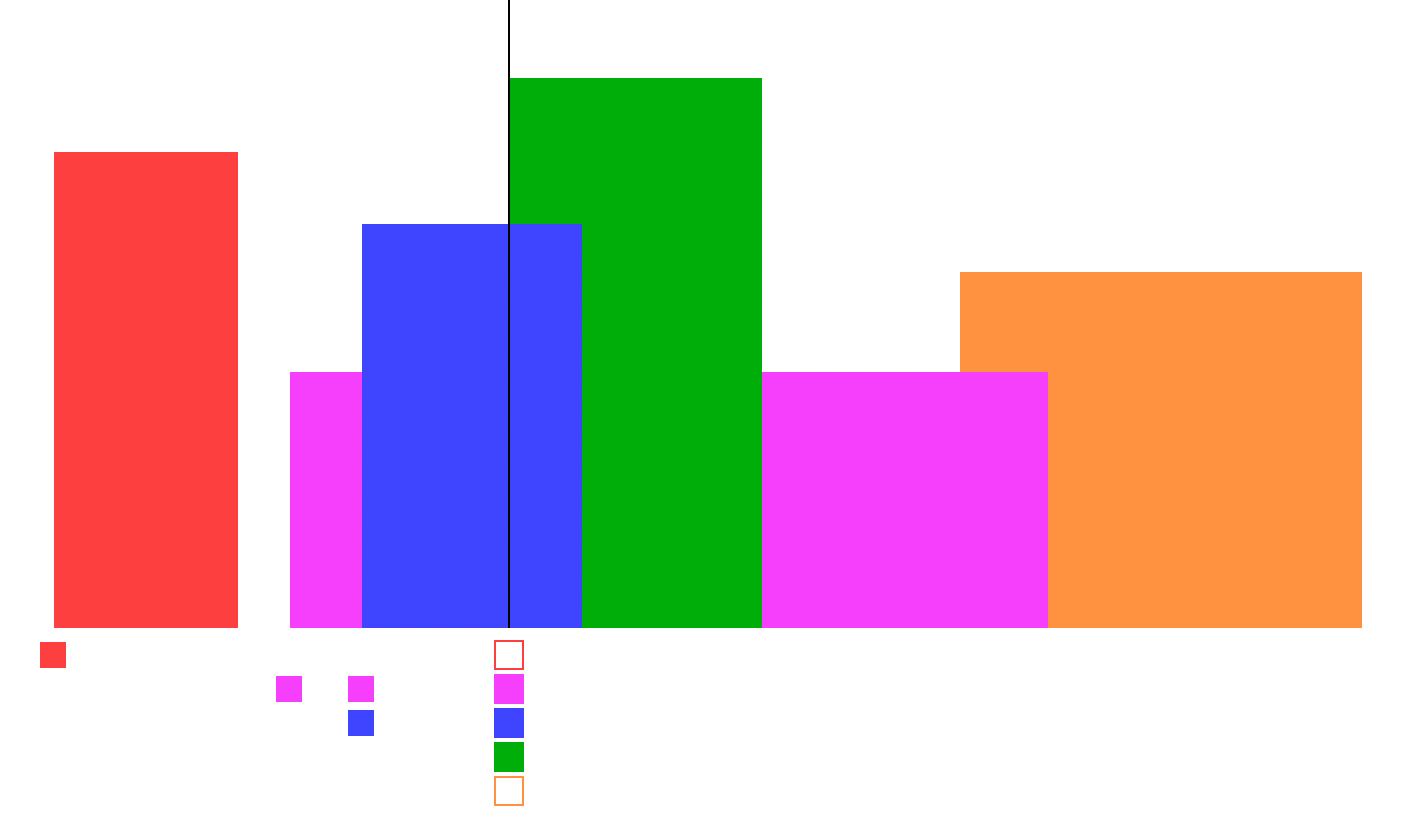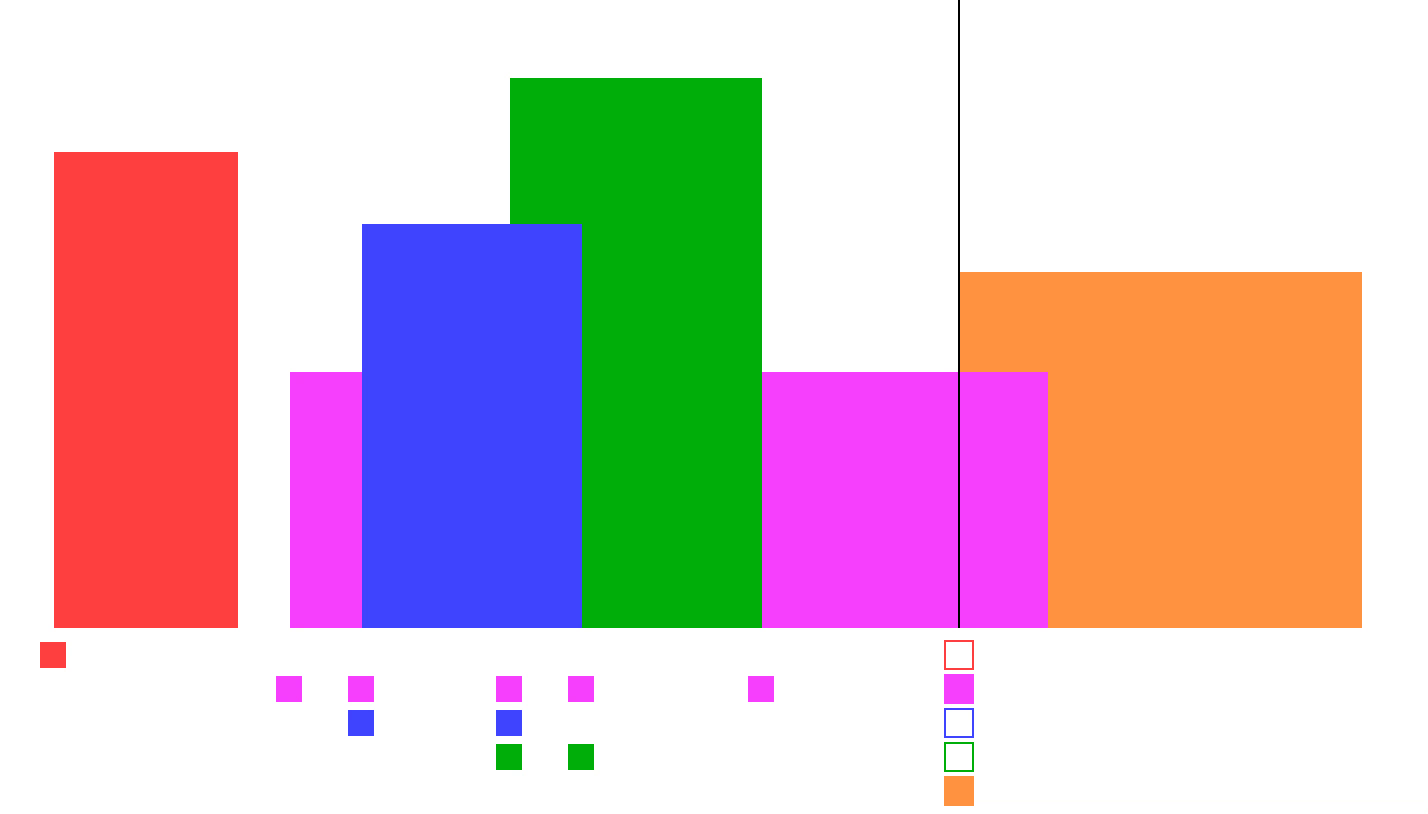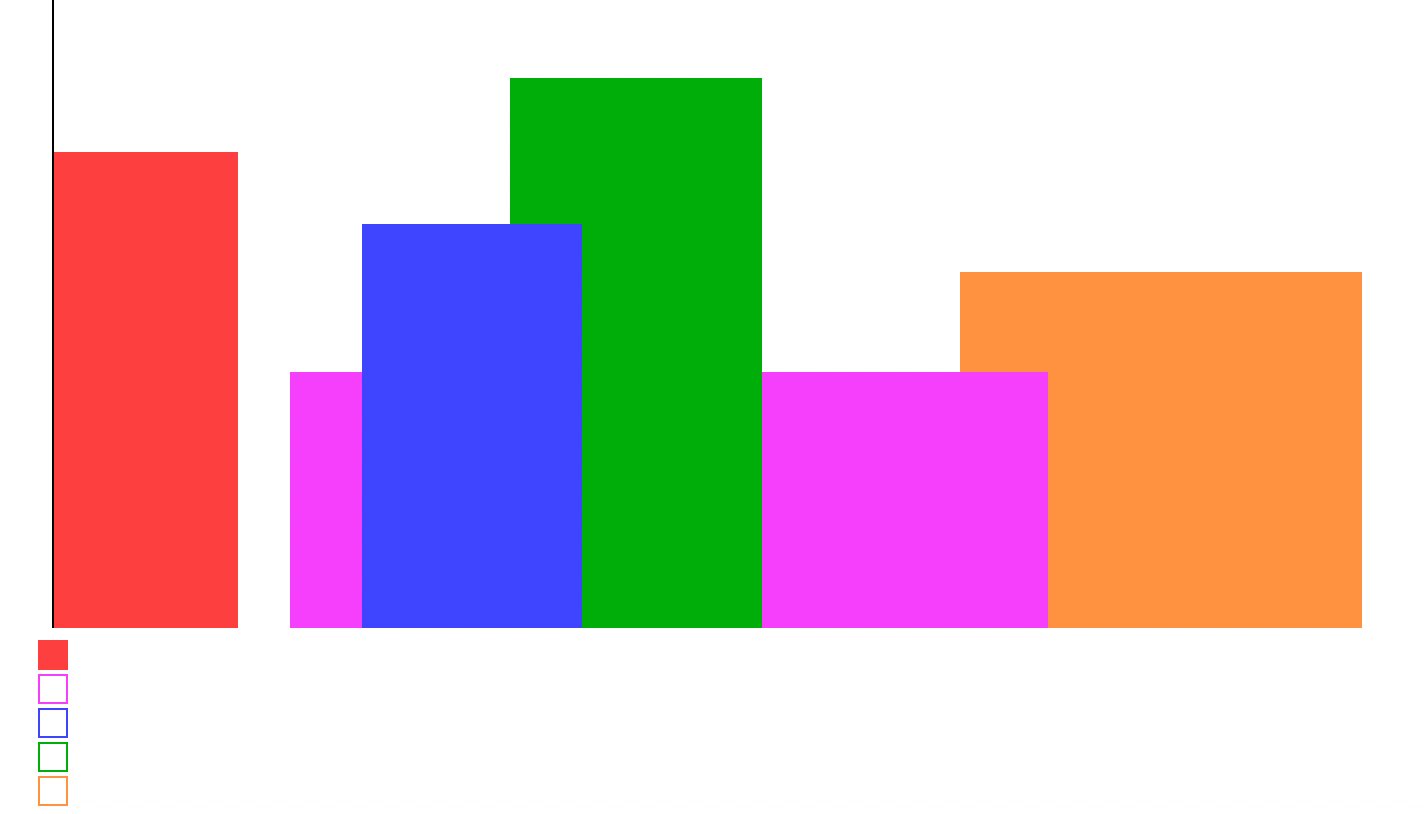
| |