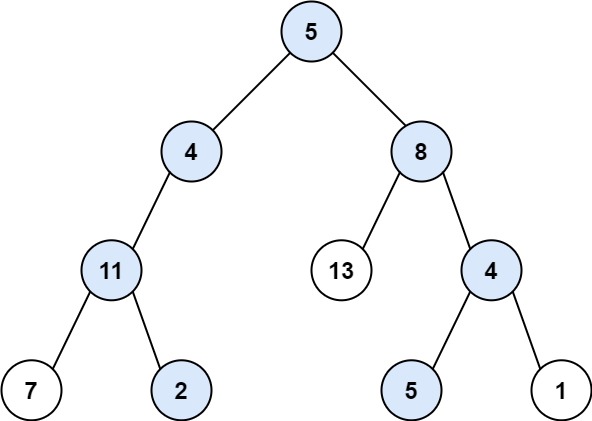
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| // @lc code=start
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
/// ## 解题思路:
/// 中序递归遍历整颗树的每一个节点`node`:
/// 1. 遍历过程中,使用一个数组记录`node_path[]`遍历过的节点;
/// 2. 节点为空,不做任何处理;
/// 3. 叶子节点,且剩余target刚好为node.val, 则找到一条合法路径,
/// - 将当前节点加入到`node_path[]`;
/// - 将`node_path[]`加入到结果集`res[]`中;
/// - 将当前节点从`node_path[]`中弹出;
/// 4. 其他情况:
/// - 4.1 将当前节点加入到路径中;
/// - 4.2 将 target_num -= node.val;
/// - 4.3 递归处理左子树;
/// - 4.4 递归处理右子树;
/// - 4.5 将节点从路径中弹出;
pub fn path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
/// helper
fn path_sum_rec(node: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target_sum: i32, node_path: &mut Vec<i32>, res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
match node {
None => {},
Some(node) if node.borrow().left.is_none() && node.borrow().right.is_none() && node.borrow().val == target_sum => {
node_path.push(node.borrow().val);
res.push(node_path.iter().cloned().collect::<Vec<_>>());
node_path.pop();
}
Some(node) => {
node_path.push(node.borrow().val);
path_sum_rec(&node.borrow().left, target_sum-node.borrow().val, node_path, res);
path_sum_rec(&node.borrow().right, target_sum-node.borrow().val, node_path, res);
node_path.pop();
}
}
}
let mut res: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![];
let mut node_path: Vec<i32> = vec![];
path_sum_rec(&root, target_sum, &mut node_path, &mut res);
res
}
}
// @lc code=end
|